zrender
introduce
https://github.com/ecomfe/zrender
https://deepwiki.com/ecomfe/zrender
echart的底层绘图渲染引擎,核心底层依赖库;
- 核心逻辑全ts实现,ts代码量31184行;
$ tokei
===============================================================================
Language Files Lines Code Comments Blanks
===============================================================================
CSS 1 94 73 18 3
JavaScript 19 19376 18842 223 311
JSON 7 13330 13321 0 9
Markdown 2 56 0 37 19
SVG 2 28 22 3 3
TypeScript 136 31184 22357 4612 4215
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HTML 78 1929 1623 121 185
|- CSS 35 550 545 2 3
|- JavaScript 78 8147 6919 369 859
(Total) 10626 9087 492 1047
===============================================================================
Total 245 65997 56238 5014 4745
- 这个库没有dependencies: 业务逻辑依赖均自身实现;devDependencies主要用来打包和定制化脚本;
调试方法
npm run watch:bundle: 构建本地版本的zrender,生成dist/zrender.js文件;- 浏览器可直接打开本地的test文件夹下的html,使用绝对地址:
/Users/jie3131/Documents/github/zrender/test/animation-keyframe-easing.html, 即可开始调试流程;
调试zrender绘制基本流程
- 简化版调用代码示例:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Animation Keyframe Easing</title>
<script src="../dist/zrender.js"></script>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<style>
html,
body,
#main {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var main = document.getElementById("main");
// 初始化zrender
var zr = zrender.init(main);
let i = 0;
var circle = new zrender.Circle({
x: 100,
y: i * 80,
shape: {
cx: 30,
cy: 30,
r: 30,
},
style: {
fill: "red",
lineWidth: 5,
},
});
zr.add(circle);
</script>
</body>
</html>
主要调试
zr.add(circle)的流程,关键执行过程:
zrender:zr.add()=>this.refresh()=>animation.start()=>this.stage.update()
animation:animation.start()=>_startLoop()=>self.update()=>this.stage.update()(animation的stage在zrender的constructor中初始化)
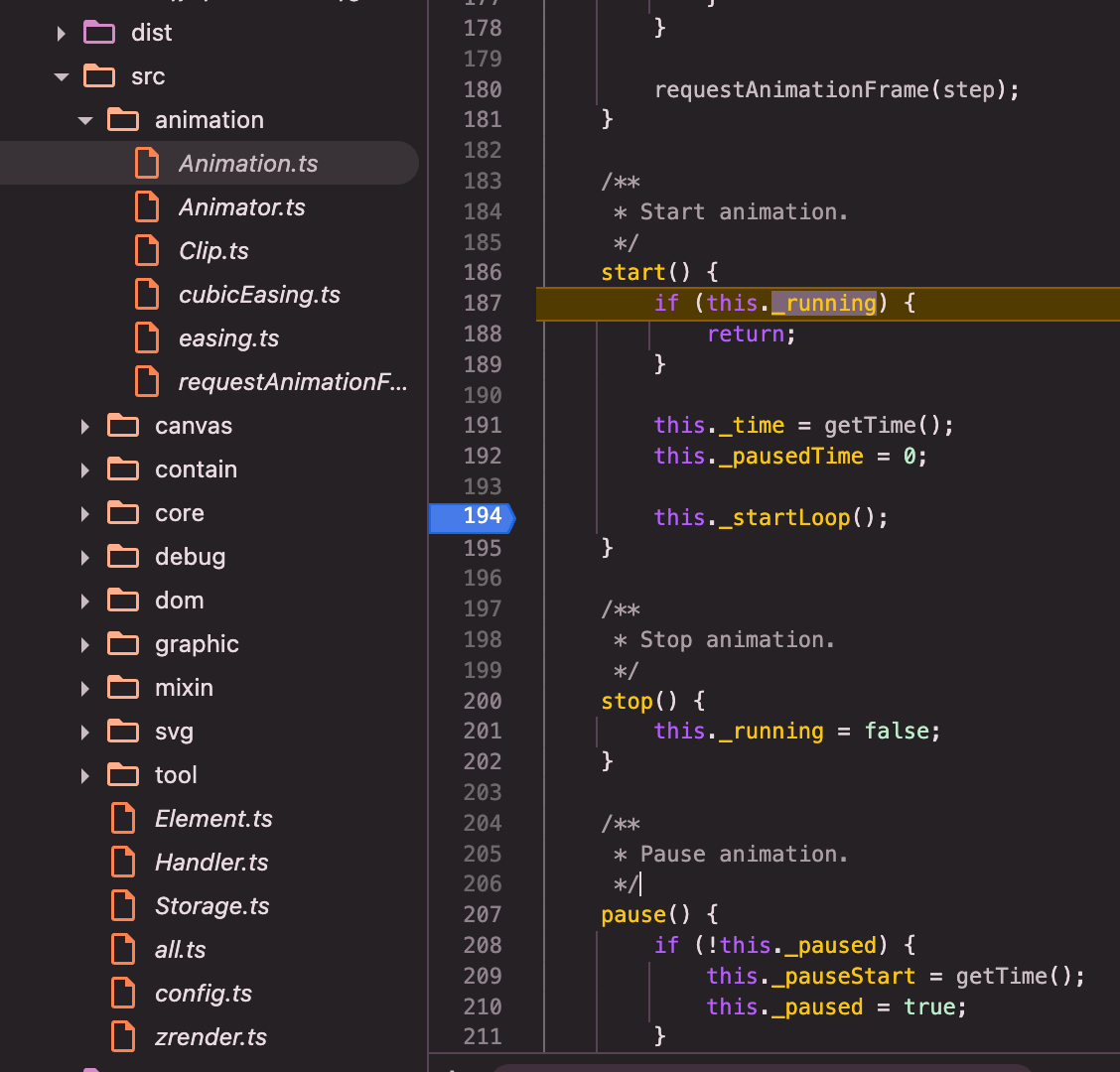
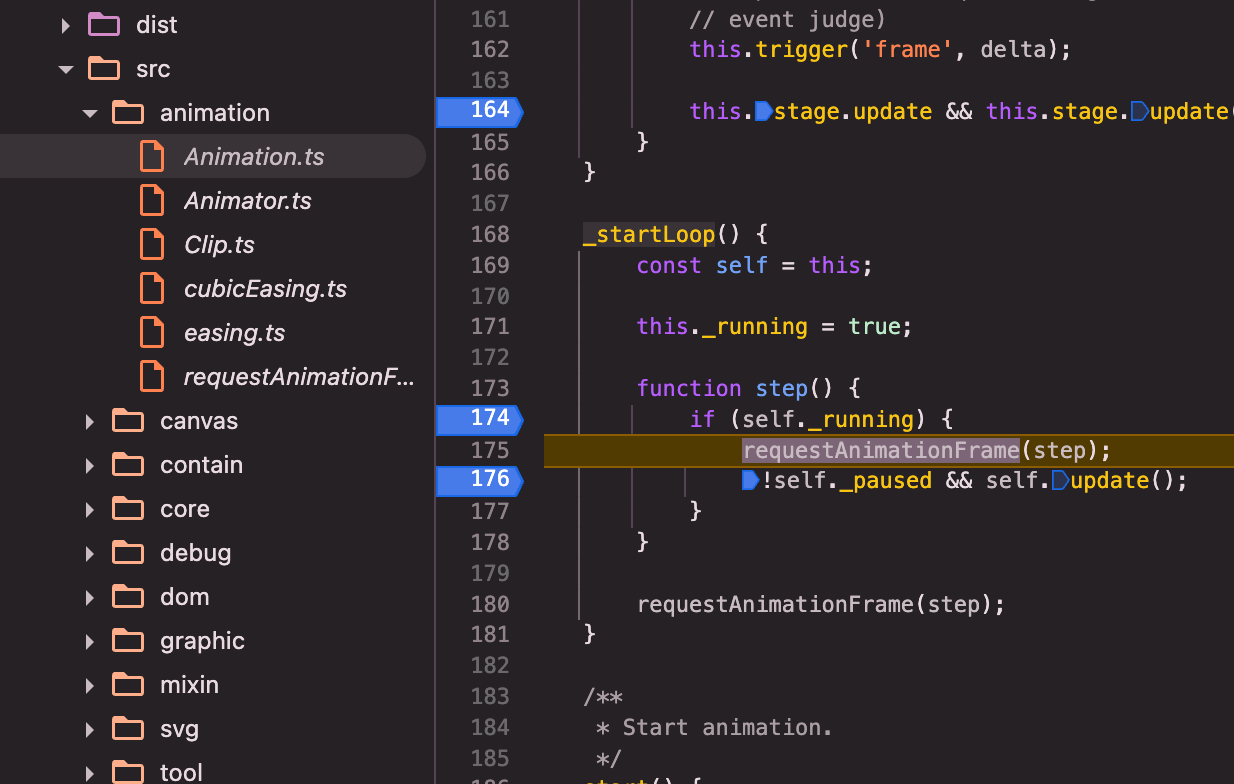
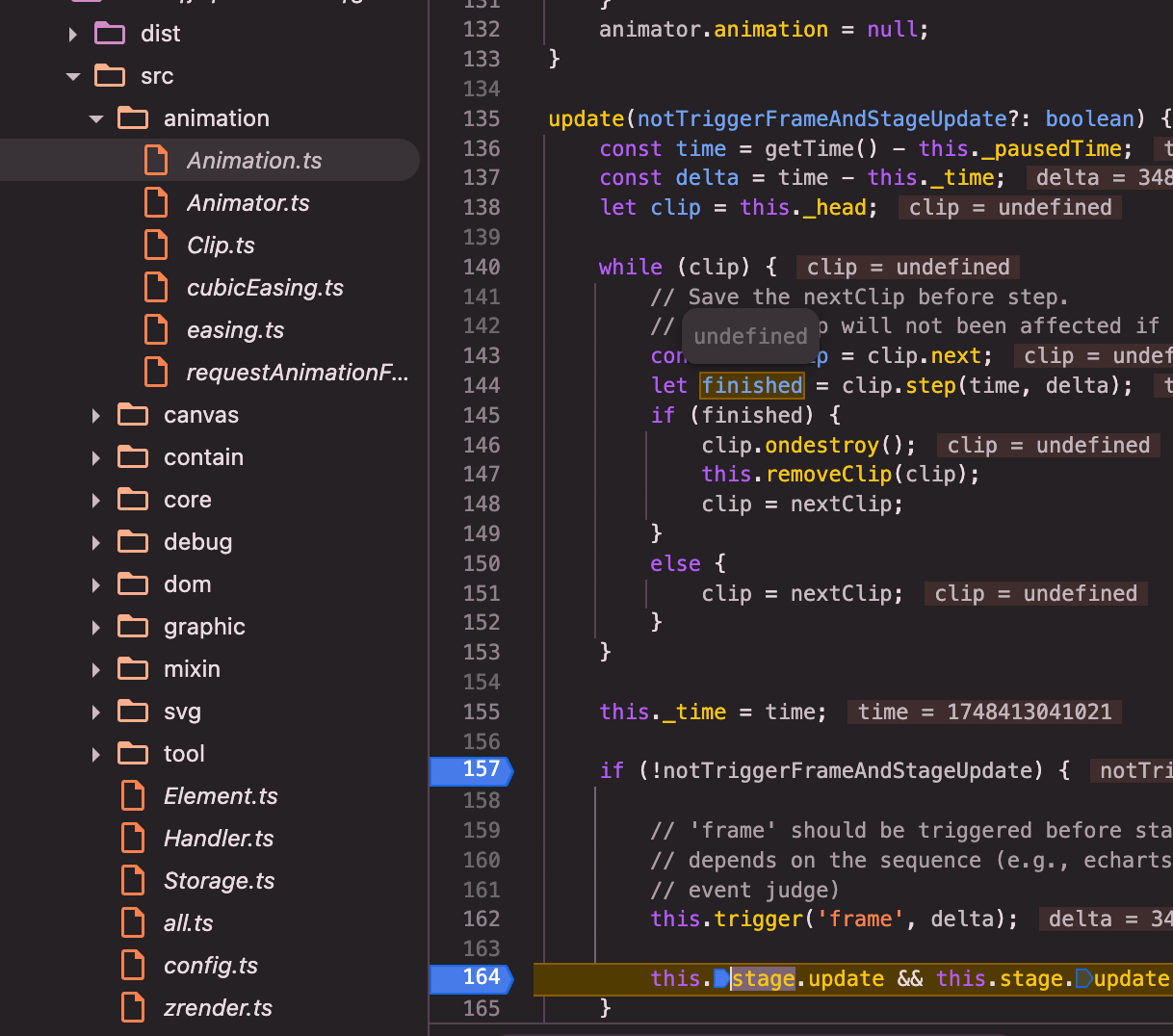
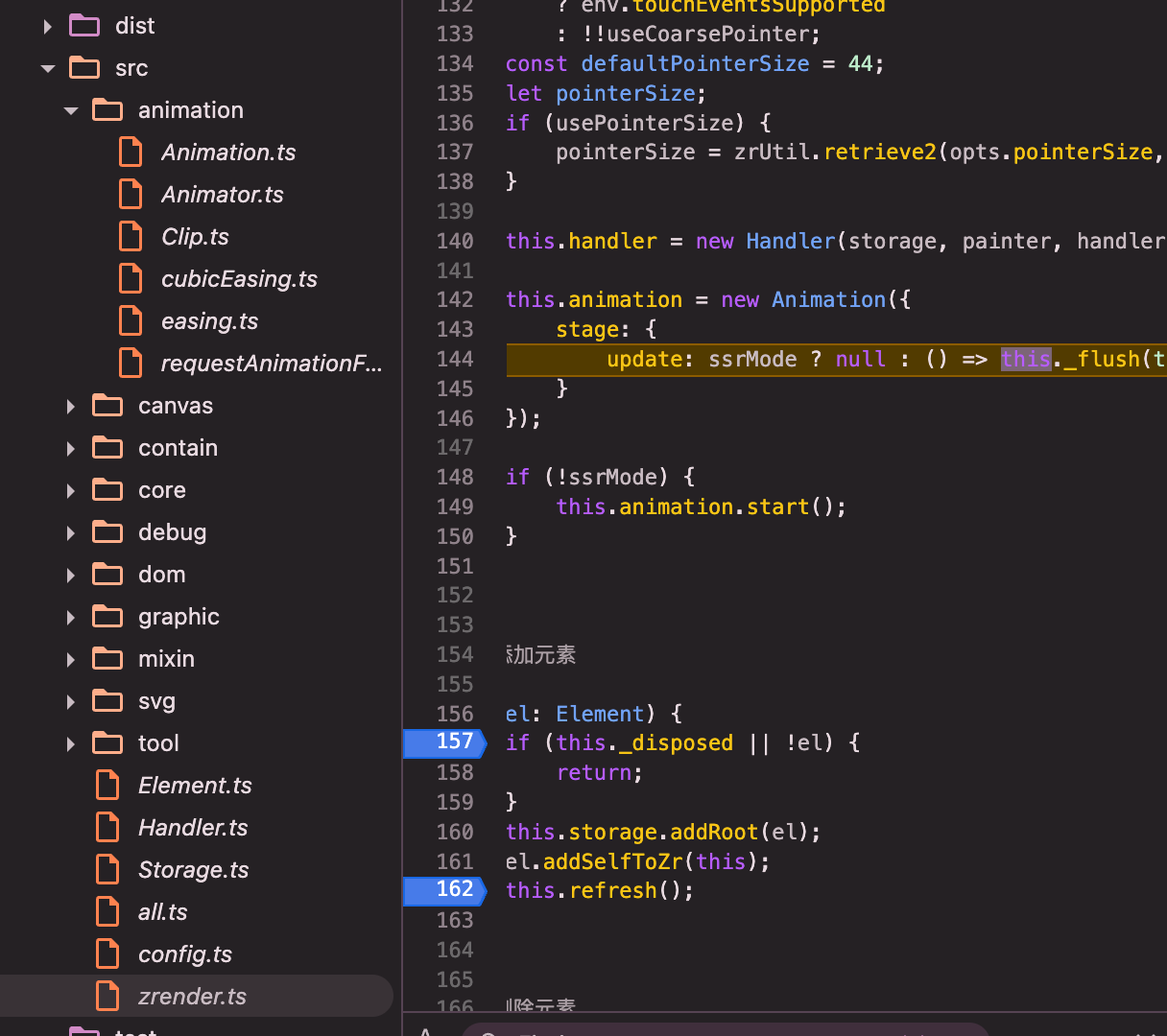
zrender:constructor赋值:annimation.stage.update为_flush()=>_flush()=>refreshImmediately()=>this.painter.refresh();
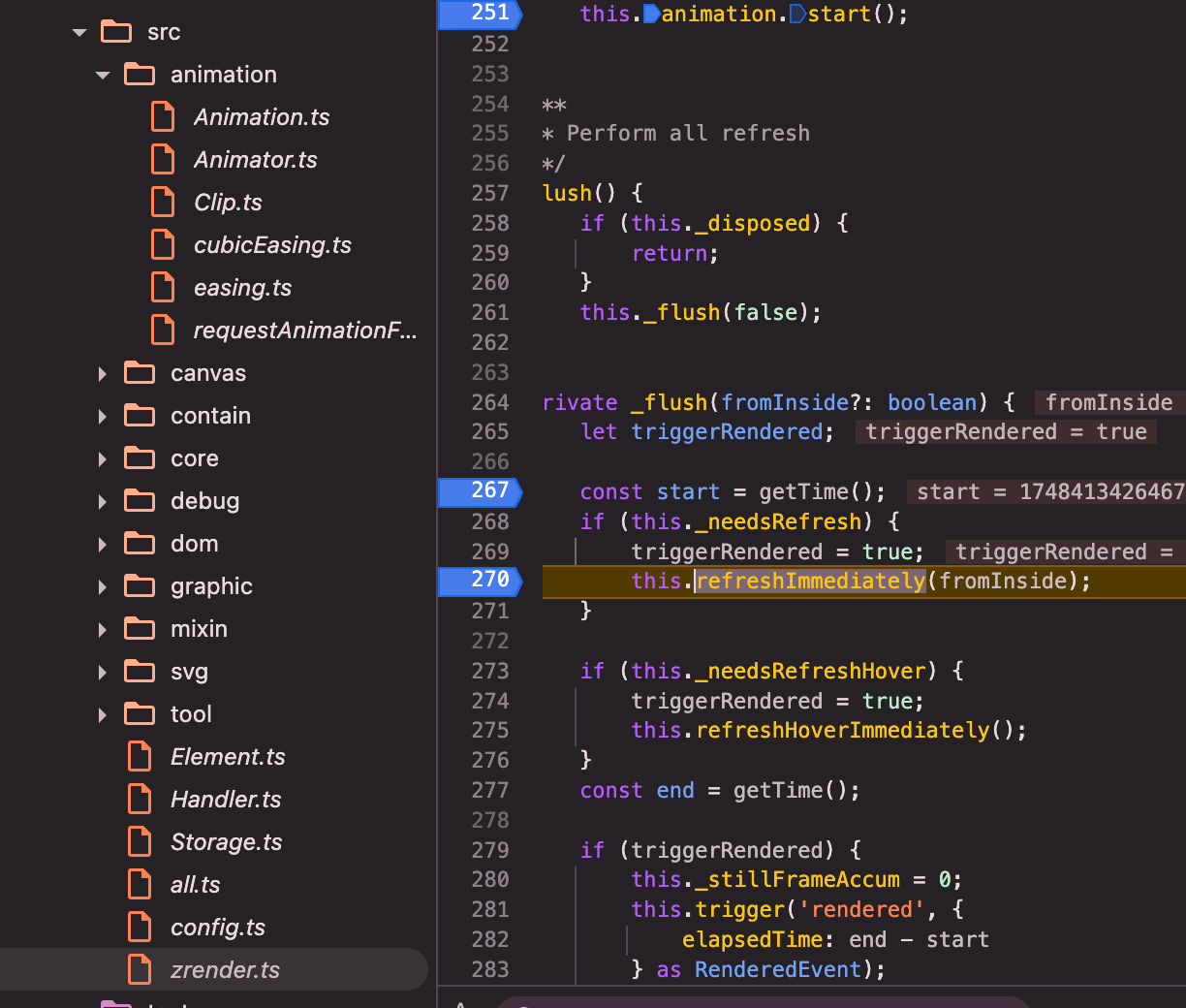
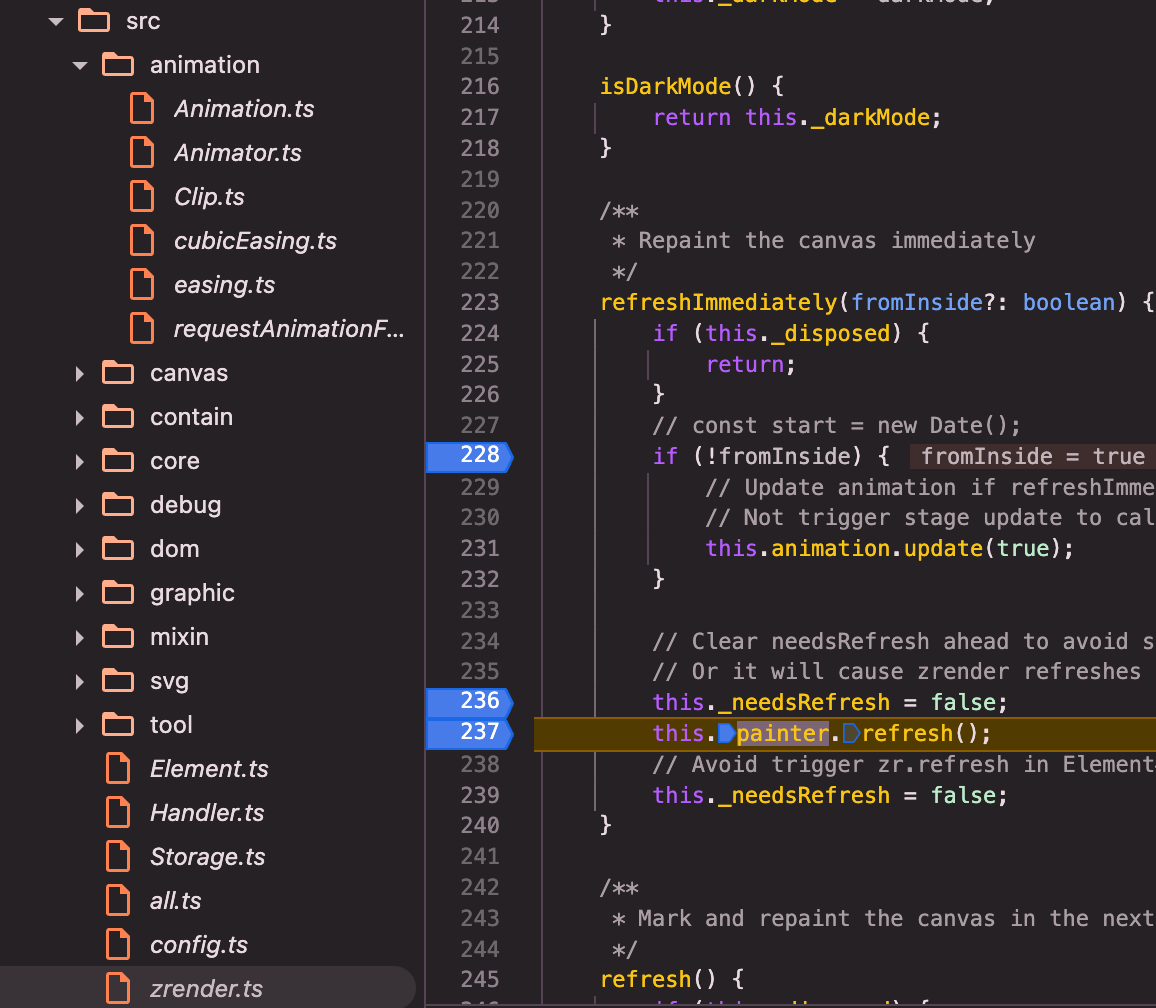
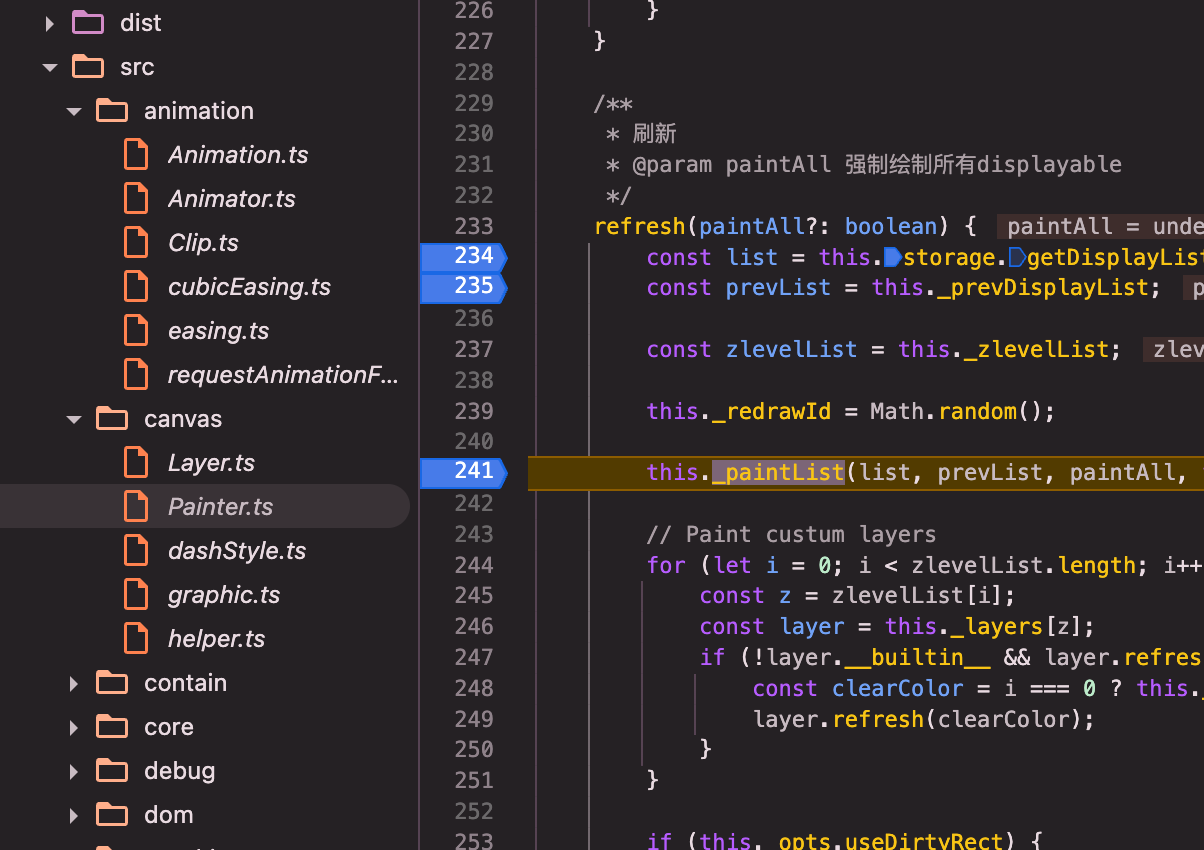
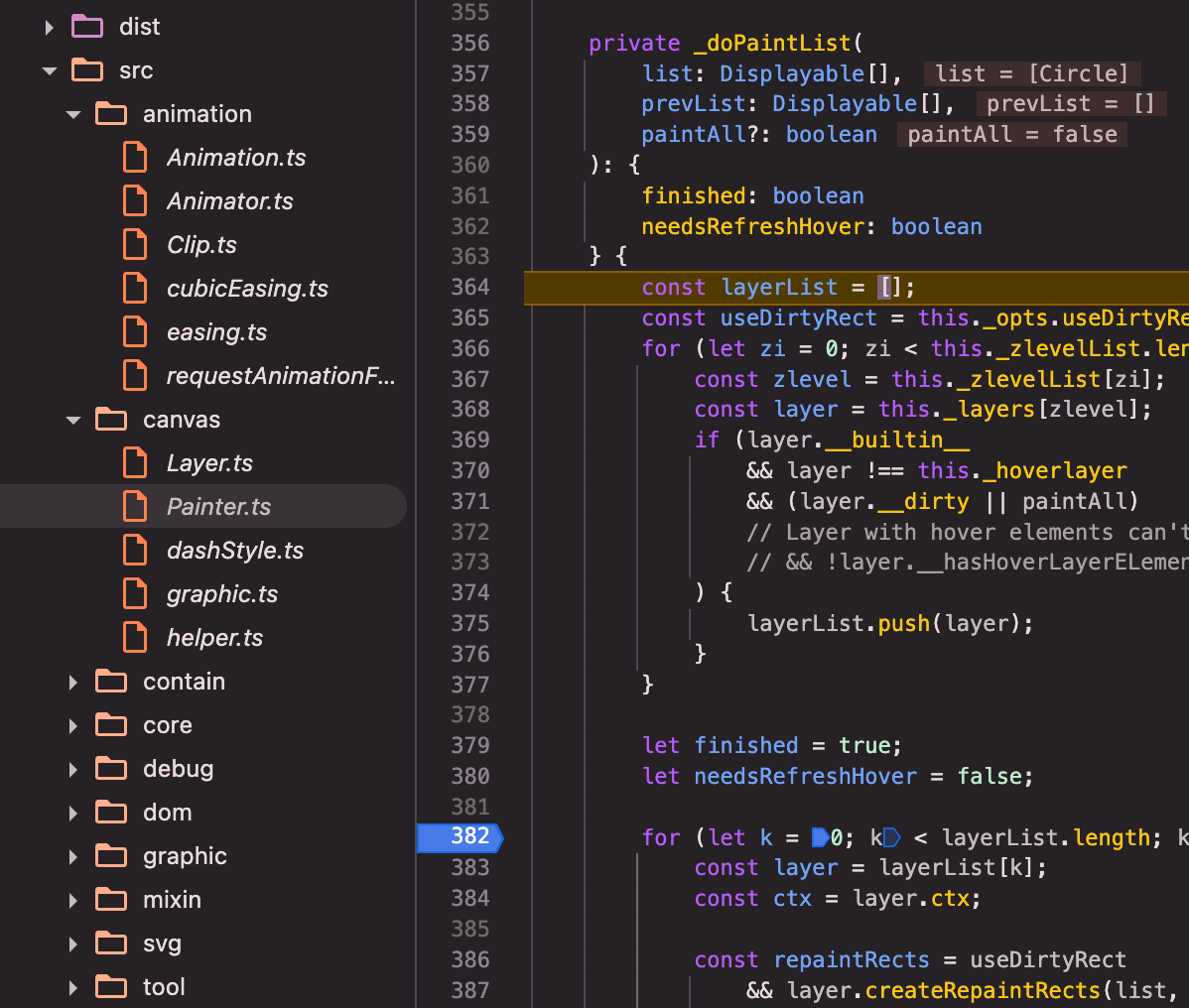
painter(以canvas painter为例src/canvas/Painter.ts):refresh()=>_paintList()=>_doPaintList()=>_doPaintList内部闭包repaint()=>_doPaintEl()=>brush()
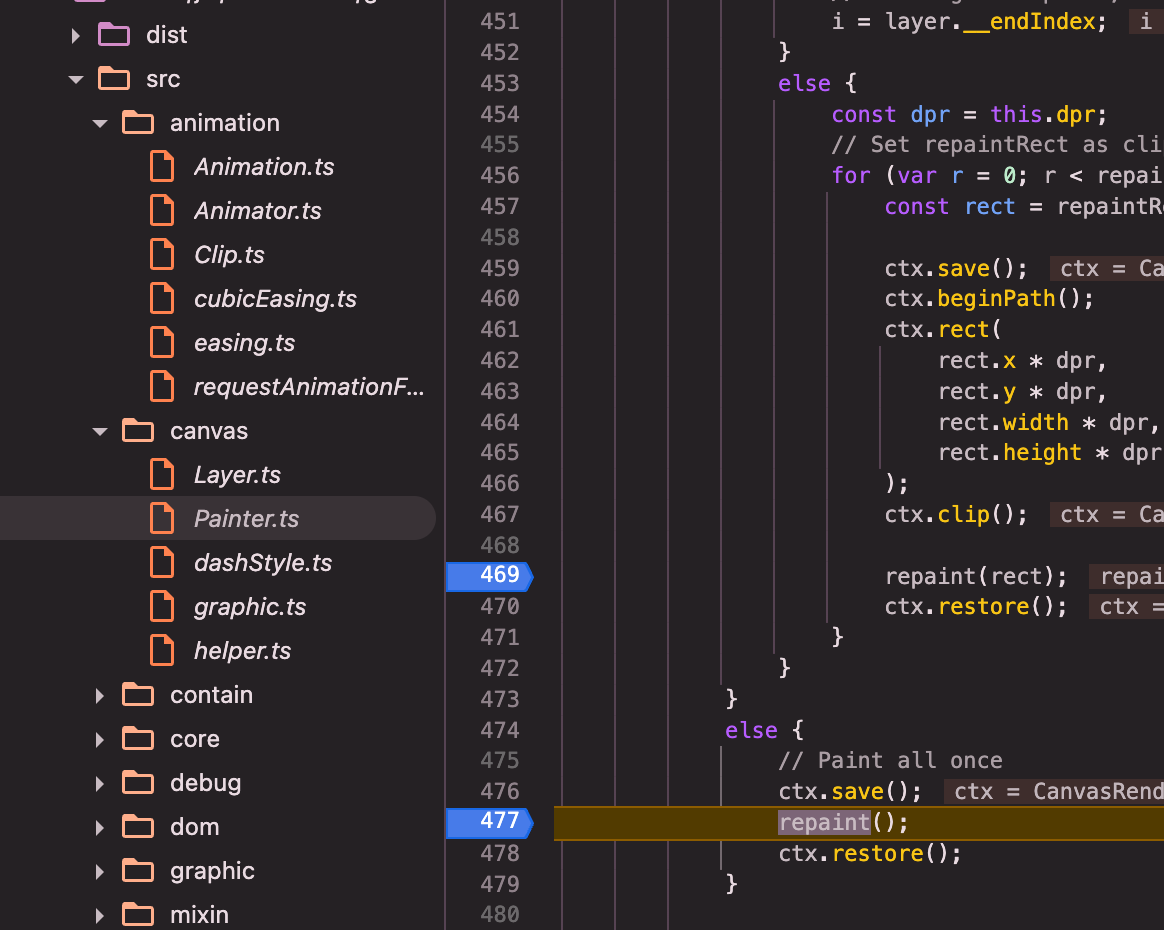
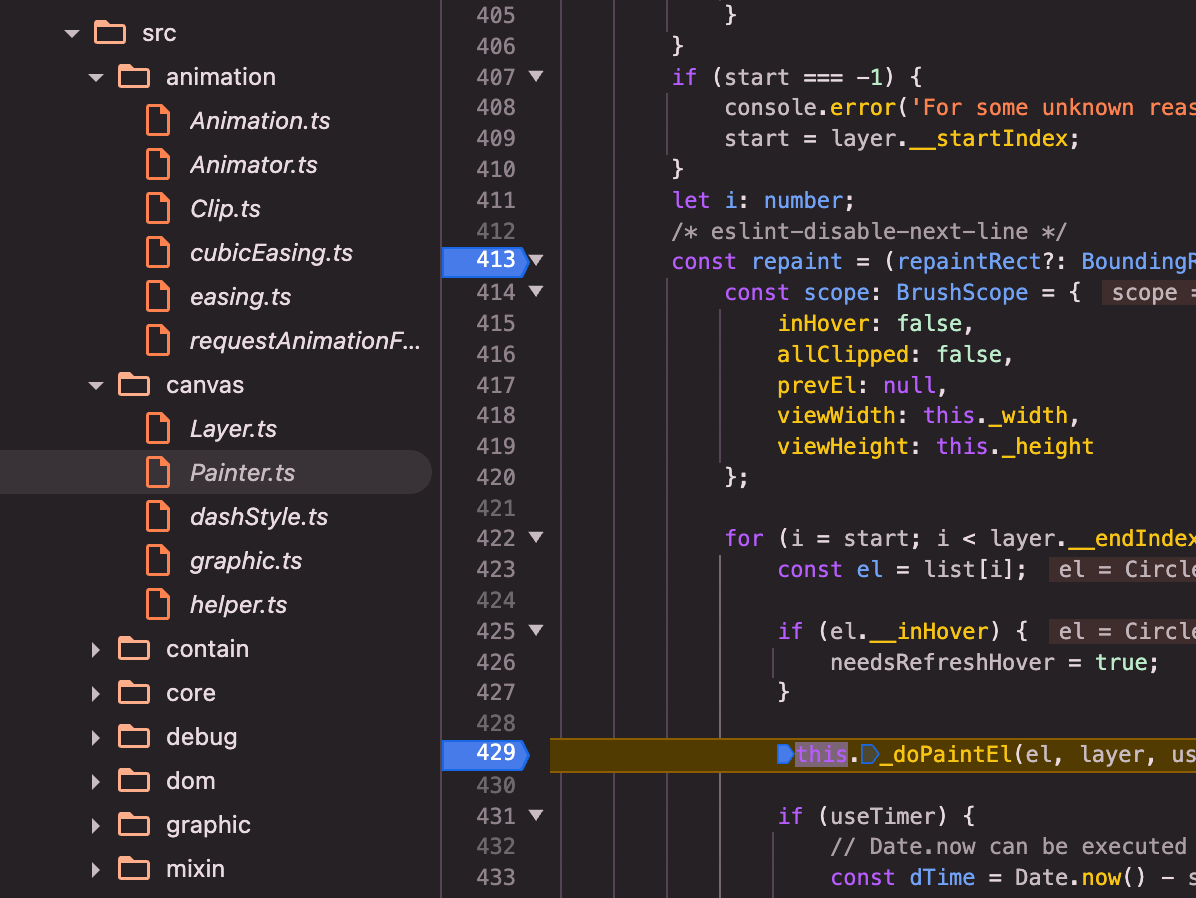
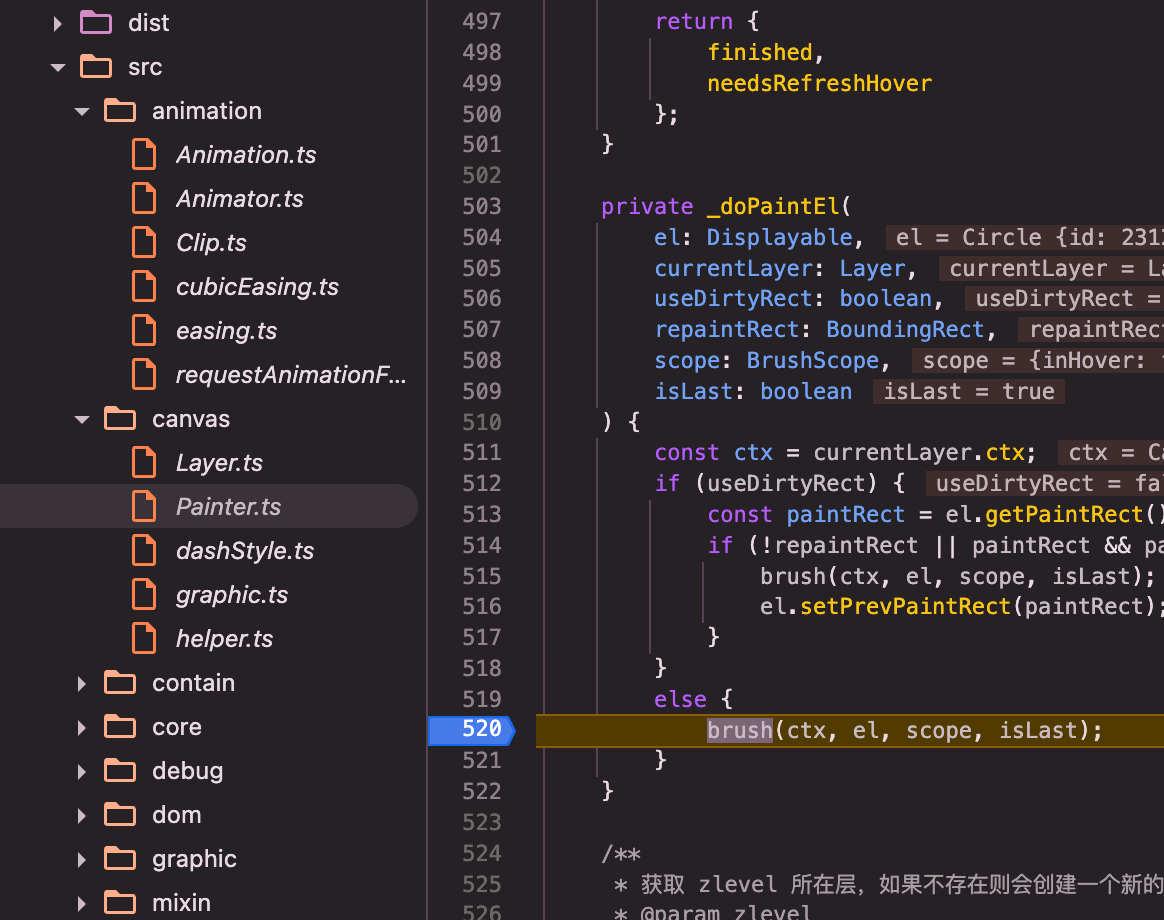
brush()(canvas的brush,src/canvas/graphic.ts):brush()=> bursh内部调用brushPath()=>brushPath()=> brushPath内部关键调用el.buildPath(path, el.shape, inBatch);
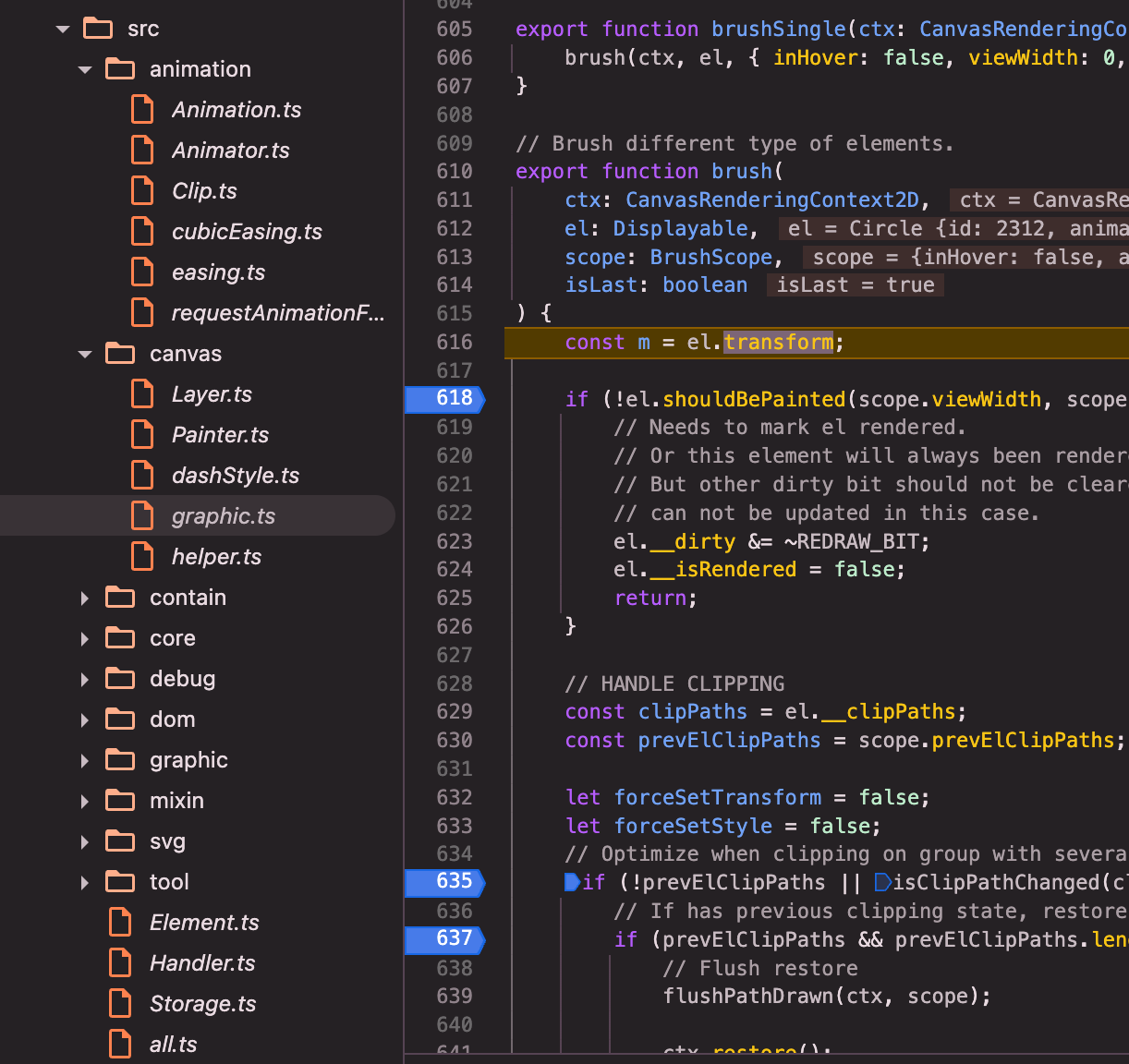
buildPath(): path中定义buildPath接口=> 以Circle这种Path的子类为例,具体实现buildPath()(调用canvas方法,具体实现绘制方法)
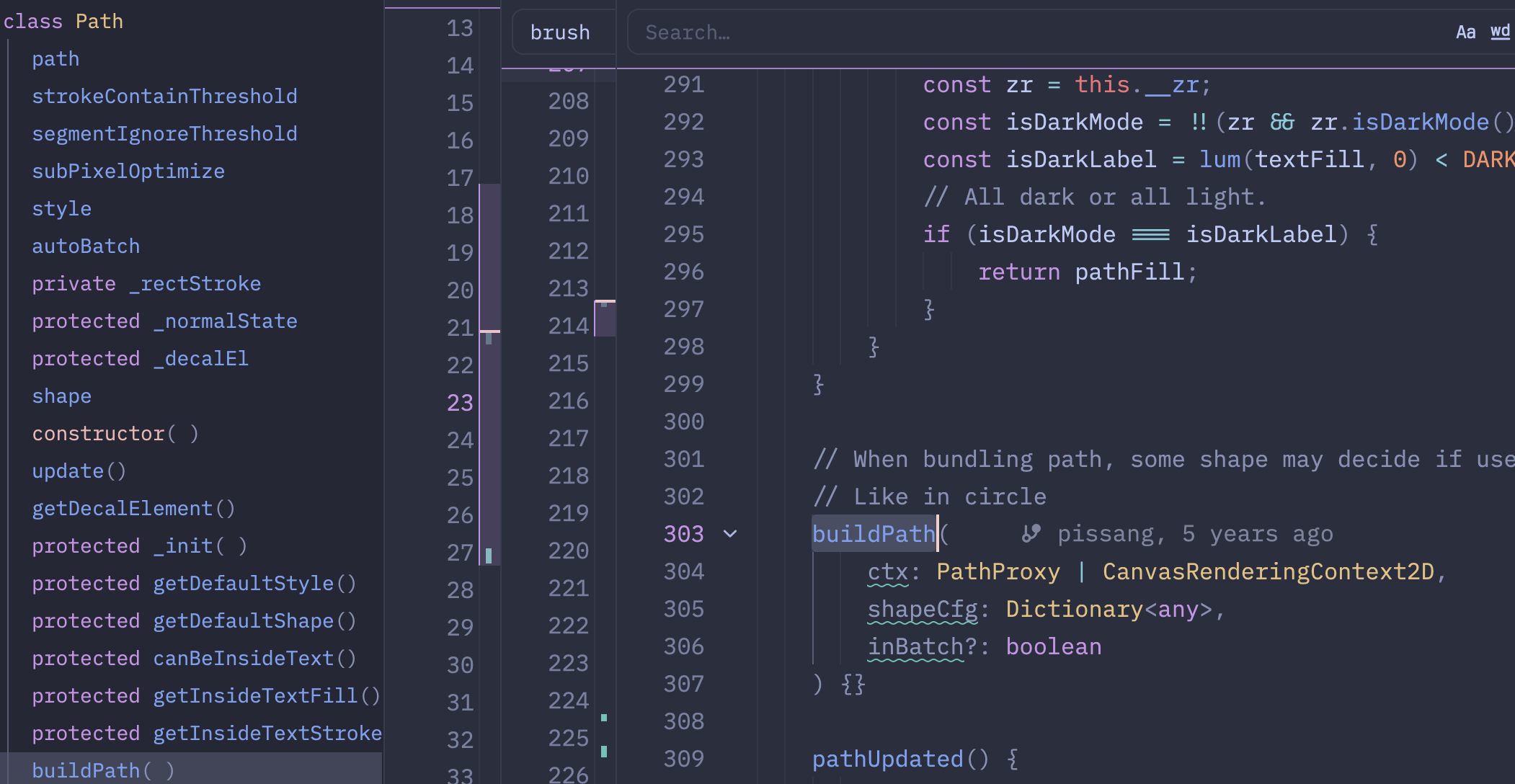
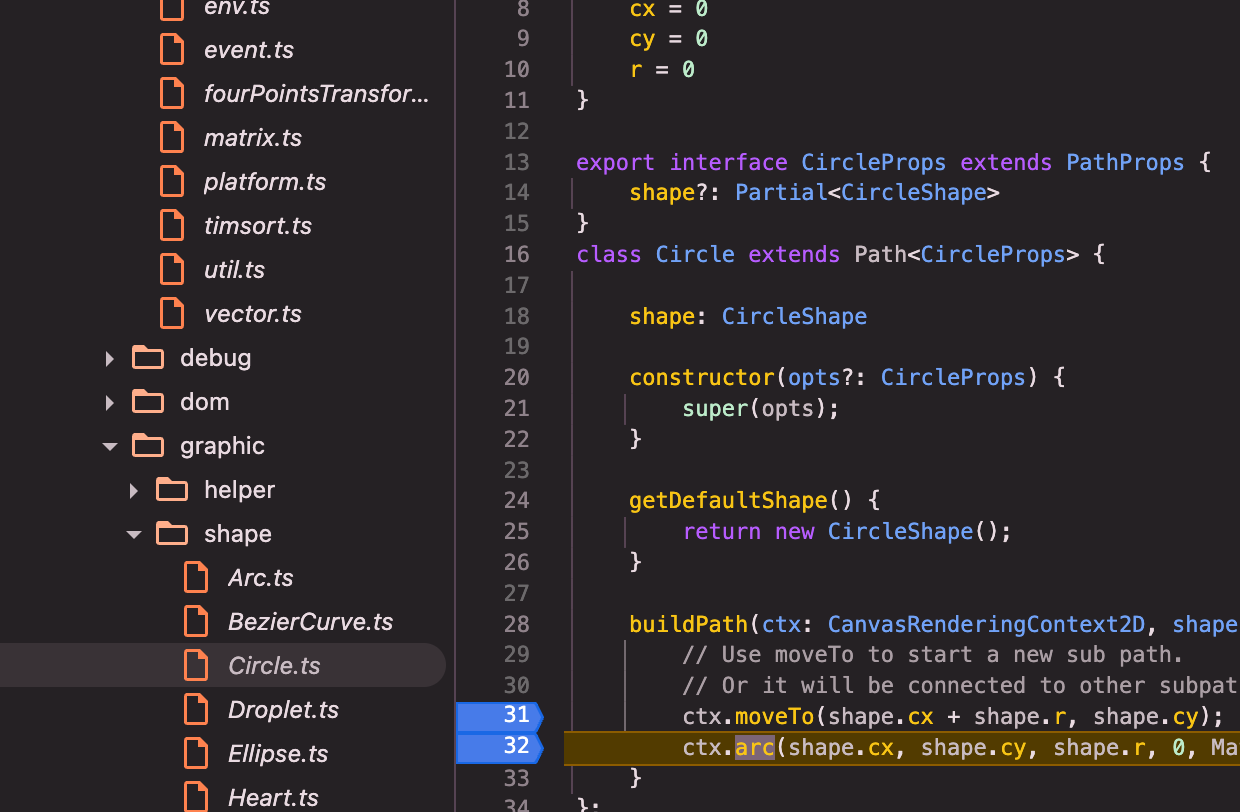
图形的绘制,主要是调用zr的_flush()方法实现
调试zrender动画流程
- 简化版调用代码示例:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Animation Keyframe Easing</title>
<script src="../dist/zrender.js"></script>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<style>
html,
body,
#main {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var main = document.getElementById("main");
// 初始化zrender
var zr = zrender.init(main);
let i = 0;
var circle = new zrender.Circle({
x: 100,
y: i * 80,
shape: {
cx: 30,
cy: 30,
r: 30,
},
style: {
fill: "red",
lineWidth: 5,
},
});
zr.add(circle);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("log, add animation");
circle
.animate("", true)
.when(
500,
{
x: 150,
},
"sinusoidalInOut",
)
.when(
1000,
{
x: 100,
},
"sinusoidalInOut",
)
.delay(i * 100)
.start();
}, 3000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
主要先调试:
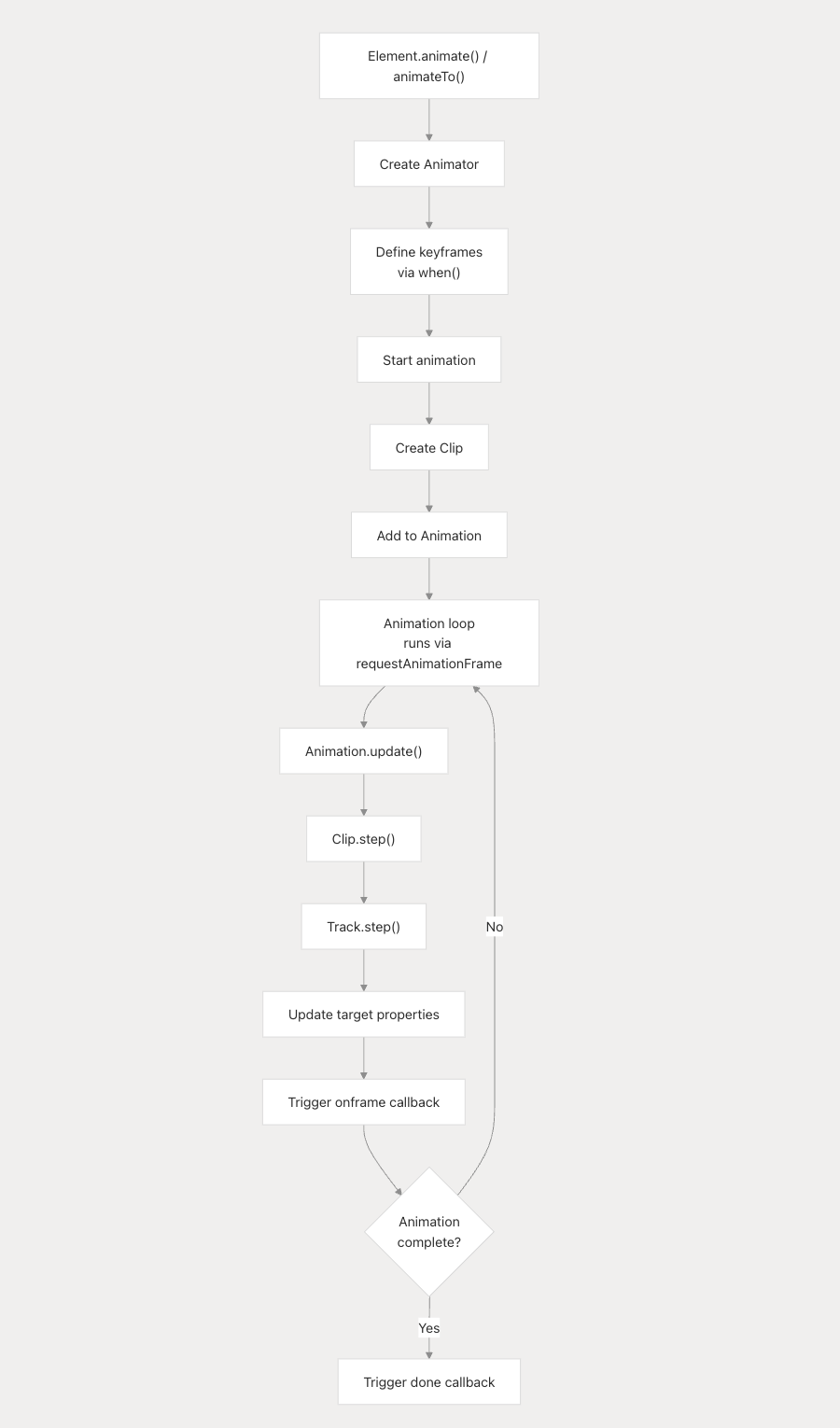
circle.animate().when().start()的流程,关键执行过程:
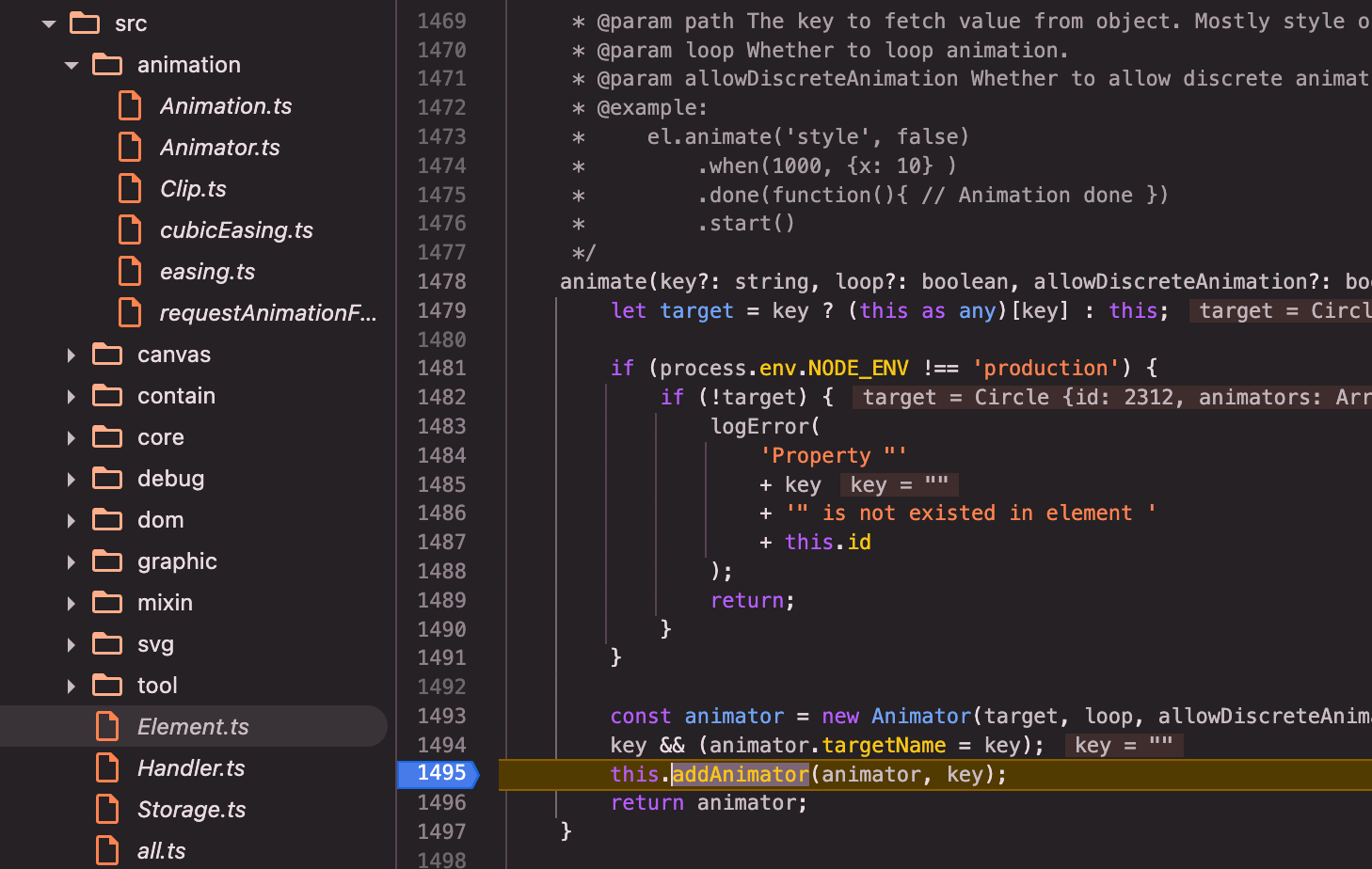
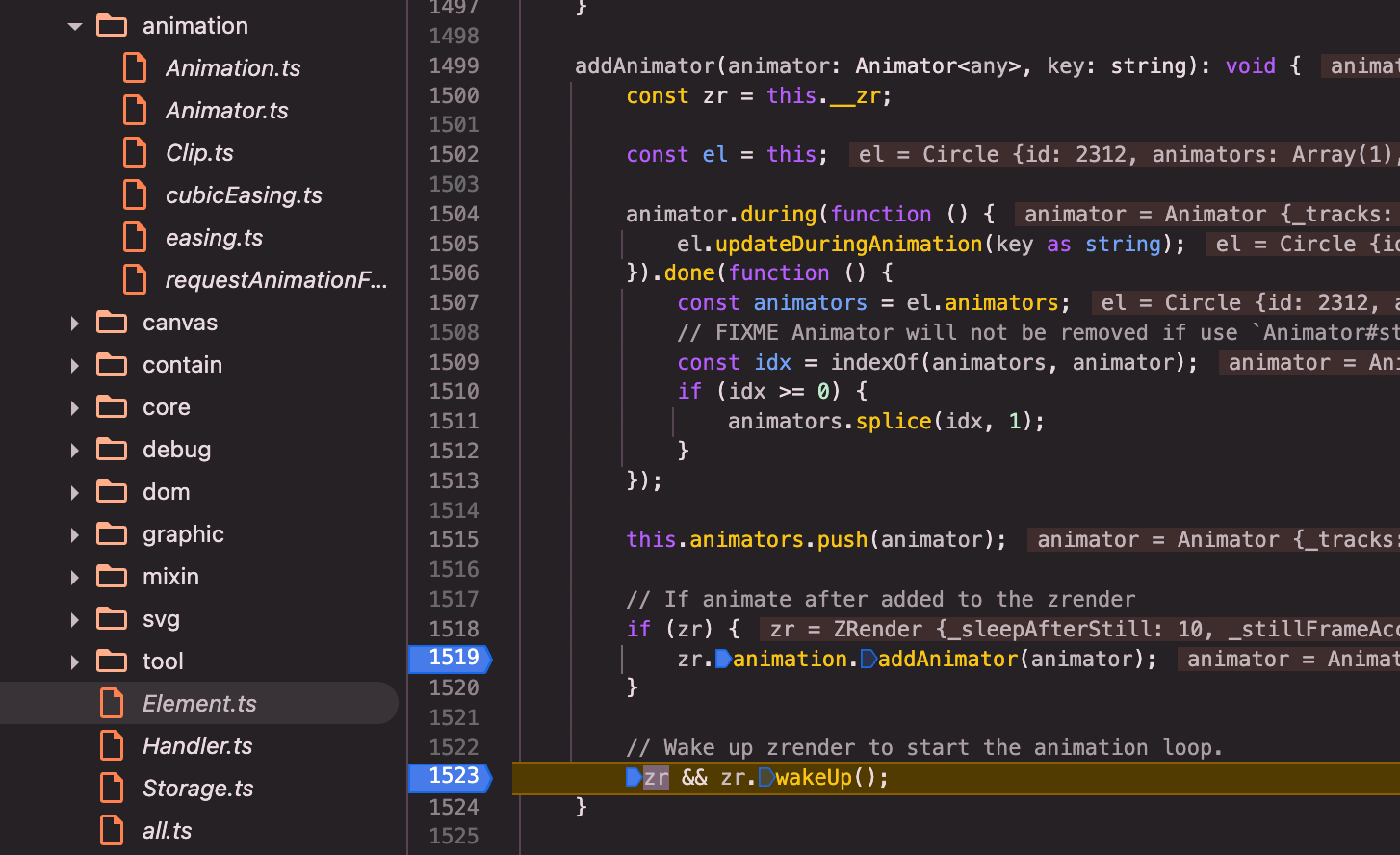
circle.animate()(circle是Element的子类):animate()=>this.addAnimator(animator, key)=> 函数内,关键调用zr.animation.addAnimator(animator)和zr && zr.wakeUp();
返回值: animate()整个函数返回的是一个
Animator对象
1.0. 详解element的:
addAnimator:
调用animator.during方法,注册el.updateDuringAnimation(key as string);刷新重绘元素的回调:animator.during方法将回调存储在_onframeCbs中,在后文animator.start()中,新建的clip对象的onframe方法中会调用这个回调函数来更新元素的状态。
// file: src/Element.ts
addAnimator(animator: Animator<any>, key: string): void {
...
animator.during(function () {
el.updateDuringAnimation(key as string);
}).done(function () {
const animators = el.animators;
// FIXME Animator will not be removed if use `Animator#stop` to stop animation
const idx = indexOf(animators, animator);
if (idx >= 0) {
animators.splice(idx, 1);
}
});
...
}
1.1. 详解zr的
addAnimator: src/animation/Animation.ts
// src/animation/Animation.ts
addAnimator(animator: Animator<any>) {
animator.animation = this;
const clip = animator.getClip();
if (clip) {
this.addClip(clip);
}
}
1.2. 调用
addClip: 每个元素的每个animator都会生成一个clip, clip在zr的animation中通过链表结构来管理:
// src/animation/Animation.ts
addClip(clip: Clip) {
if (clip.animation) {
// Clip has been added
this.removeClip(clip);
}
if (!this._head) {
this._head = this._tail = clip;
}
else {
this._tail.next = clip;
clip.prev = this._tail;
clip.next = null;
this._tail = clip;
}
clip.animation = this;
}
1.3 zr的
wakeUp: 关键调用this.animation.start()来开启requestAnimationFrame动画循环
// src/zrender.ts
wakeUp() {
if (this._disposed) {
return;
}
this.animation.start();
// Reset the frame count.
this._stillFrameAccum = 0;
}
1.4.
animation.start():start()=>_startLoop()=>self.update()=> update遍历链表,调用clip.step(time, delta)
// file: src/animation/Animation.ts
// animation中的帧动画渲染逻辑
_startLoop() {
const self = this;
this._running = true;
function step() {
if (self._running) {
requestAnimationFrame(step);
!self._paused && self.update();
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(step);
}
帧动画渲染的实现:
clip.step(time, delta), 通过链表结构管理动画的关键帧clip对象,每个clip实现了step方法,传delta来按照百分比来进行插值动画绘制;
// file: src/animation/Animation.ts
update(notTriggerFrameAndStageUpdate?: boolean) {
...
...
const time = getTime() - this._pausedTime;
const delta = time - this._time;
let clip = this._head;
while (clip) {
// Save the nextClip before step.
// So the loop will not been affected if the clip is removed in the callback
const nextClip = clip.next;
let finished = clip.step(time, delta);
if (finished) {
clip.ondestroy();
this.removeClip(clip);
clip = nextClip;
}
else {
clip = nextClip;
}
}
...
...
}
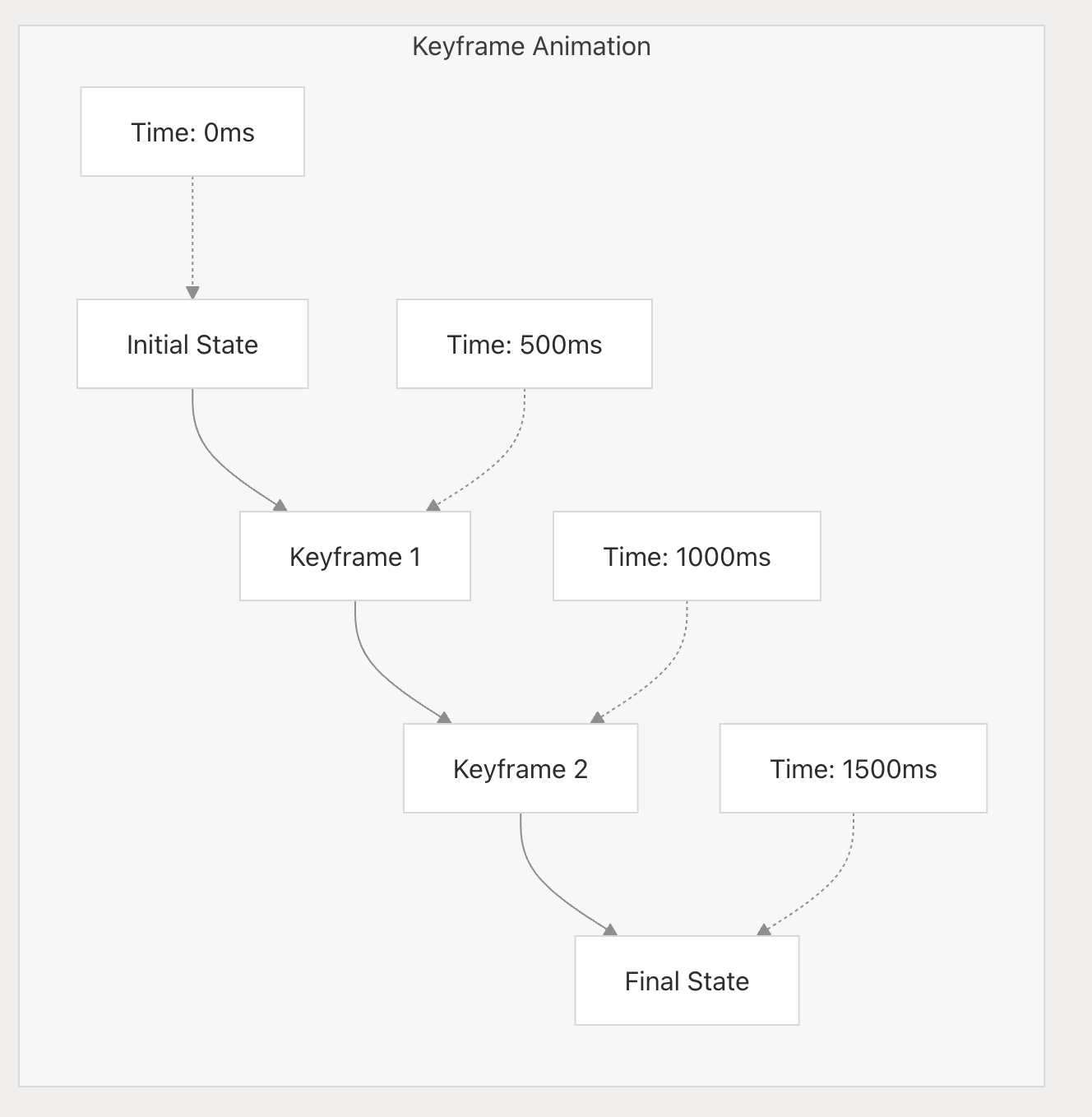
circle.animate().when().start():when(): 链接调用返回本身 => when内部调用this._addKeyframe(keyframe):将动画信息存入this._tracks=>start:
// src/animation/Animator.ts
start(easing?: AnimationEasing) {
...
if (tracks.length || this._force) {
const clip = new Clip({
...
onframe(percent: number) {
...
}
...
})
...
if (this.animation) {
this.animation.addClip(clip);
}
...
}
这clip的实现中:step中的关键调用
onframe即是在animator.start()中newClip时传入的onframe函数,clip的step方法会在每一帧调用这个函数来执行动画插值计算, clip的step的调用在上文解析中的animation.update()中遍历链表时调用的. (注意: 虽然circle.animate()中嵌套调用animation.update()会在circle.animate().when().start()的start前执行, 但在实际执行时,clip的step会在下一帧才会执行, 因为animation.start()中是通过requestAnimationFrame来实现的)
// src/animation/Clip.ts
step(globalTime: number, deltaTime: number): boolean {
...
this.onframe(schedule);
...
}
- 动画刷新机制: 在上文解析中
animation.start()开启帧动画渲染后,类似调试简单绘制过程,同样会调用:brush()=>brushPath()=>path.rebuildPath(ctx, strokePart ? strokePercent : 1);(在文件src/canvas/graphic.ts中) (rebuildPath这个方法比较典型, 其实也有其它子函数绘制逻辑,跟分层绘制、坐标变化等等有关)
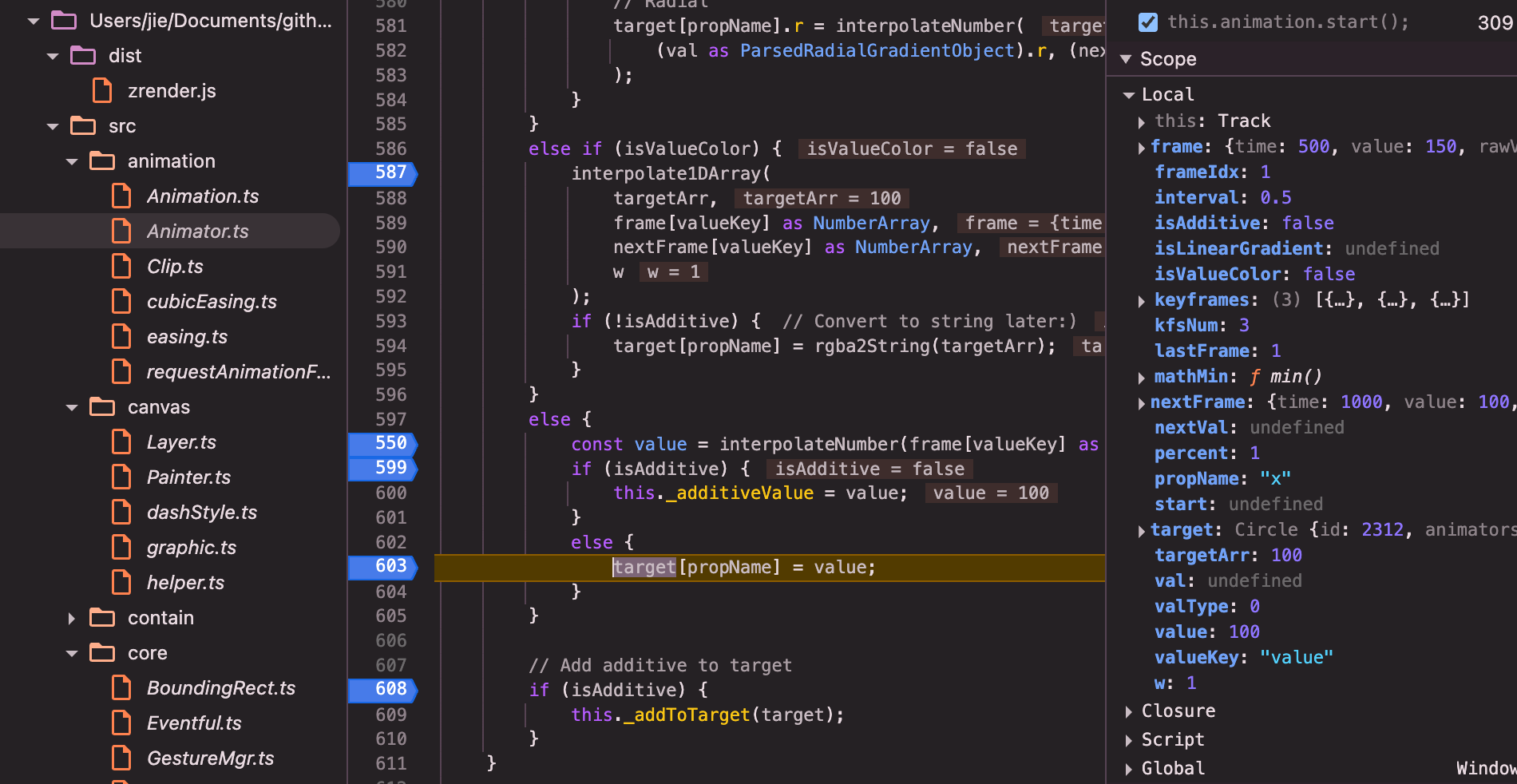
插值动画属性的计算是在:
src/animation/Animator.ts中,animator.start()的new Clip的onframe回调中,调用tracks[i].step(self._target, percent)来计算的
// src/animation/Animator.ts
// Track.step方法: 计算更新元素新的属性
step(target: any, percent: number) {
...
...
}
- 动画插值更新的实现: 核心相关的
src/core/PathProxy.ts和src/graphic/Path.ts的实现:
注意这个函数实现,ctx除了可以传CanvasRenderingContext2D还可以传PathProxy;在path中的部分函数会传pathProxy来实现路径的存储和绘制;
// file: src/graphic/Path.ts
// When bundling path, some shape may decide if use moveTo to begin a new subpath or closePath
// Like in circle
buildPath(
ctx: PathProxy | CanvasRenderingContext2D,
shapeCfg: Dictionary<any>,
inBatch?: boolean
) {}
在PathProxy中将ctx的相关方法实现了, 主要是
moveTo,lineTo,arc,bezierCurveTo等方法, 这些方法会将绘制的路径存储在this.data中, 最终通过ctx.addData()来添加到ctx中。 比如这个moveTo方法的实现,this.addData(CMD.M, x, y)会将路径操作数据存储
// src/core/PathProxy.ts
moveTo(x: number, y: number) {
// Add pending point for previous path.
this._drawPendingPt();
this.addData(CMD.M, x, y);
this._ctx && this._ctx.moveTo(x, y);
// x0, y0, xi, yi 是记录在 _dashedXXXXTo 方法中使用
// xi, yi 记录当前点, x0, y0 在 closePath 的时候回到起始点。
// 有可能在 beginPath 之后直接调用 lineTo,这时候 x0, y0 需要
// 在 lineTo 方法中记录,这里先不考虑这种情况,dashed line 也只在 IE10- 中不支持
this._x0 = x;
this._y0 = y;
this._xi = x;
this._yi = y;
return this;
}
在动画插值刷新的关键调用
path.rebuildPath()实现中,即是依赖这个路径操作数据
还有其它需要细节,可以借助chatgpt/deepseek回答来辅助理解
-
思考: 比如canvas怎么实现多个重叠元素中,某个一个元素的动画插值更新呢?:canvas没有元素的概念,只能清除然后重绘制,通过分层绘制来实现性能的优化:zrender 的分层设计通过:动静分离:静态内容永久缓存,局部更新:仅重绘变化区域,并行处理:多层独立渲染,资源复用:纹理/状态共享;实现了:复杂场景:流畅渲染10K+元素,动态内容:支持60FPS动画,混合渲染:Canvas2D/SVG/WebGL统一管理,这种架构使 zrender 能高效支撑 ECharts 等复杂可视化库,在保持渲染质量的同时,最大化性能表现。
-
思考:这个是zrender源码中的rebuildPath函数,帮我分析下它的作用和原理,越详细越好;在zrender的brushPath函数中,会调用rebuildPath方法,而rebuildPath方法的实现中关键用到的路径操作数据。因此想问这个路径操作数据是怎么产生的,过程是什么样的;“使用 PathProxy 的路径操作方法(如 moveTo, lineTo)”,是指在哪个地方会调用PathProxy的moveTo等方法吗;
总结:
动画的绘制,主要是调用animation的start()方法实现,通过插值和重绘每一帧实现流程的动画。 每个动画都是通过requestAnimationFrame来实现的, 这个动画引擎性能很好,感觉也比较依赖浏览器的js执行效率,这说明浏览器中js的执行效率还是很高的。
core-architecture
-
非常好的绘图引擎,全ts实现,非常值得多读几遍;
-
个人思考: 代码非常优秀,但是有点改进地方:
canvas,svg,graphic这几个目录组织不是很清晰,可能是历史原因,建议将canvas和svg的绘图逻辑抽象成一个公共的graphic目录,里面包含所有的绘图逻辑,这样可以更好地复用代码,减少重复代码量; -
class relationships:
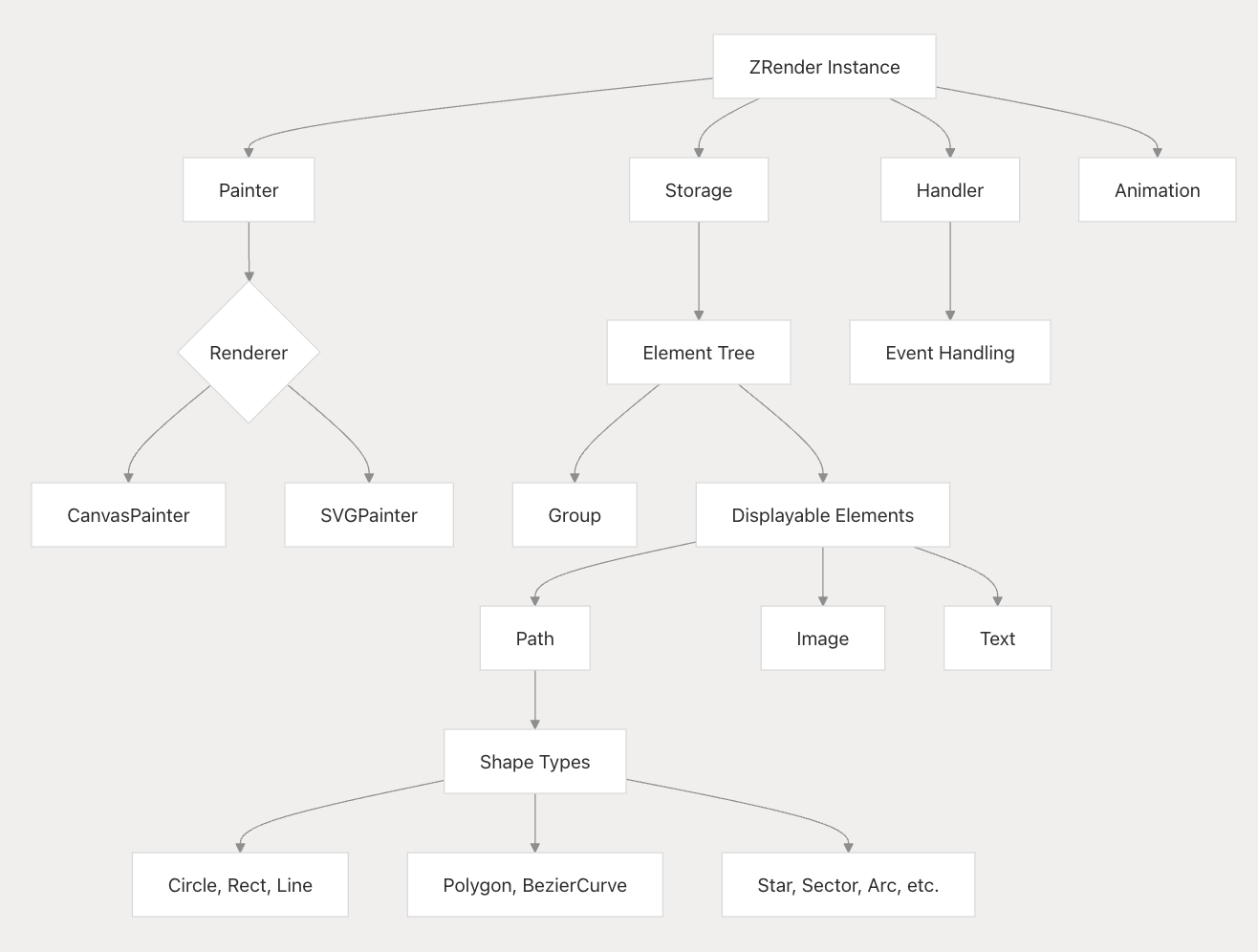
-
Initialization and Usage Flow:
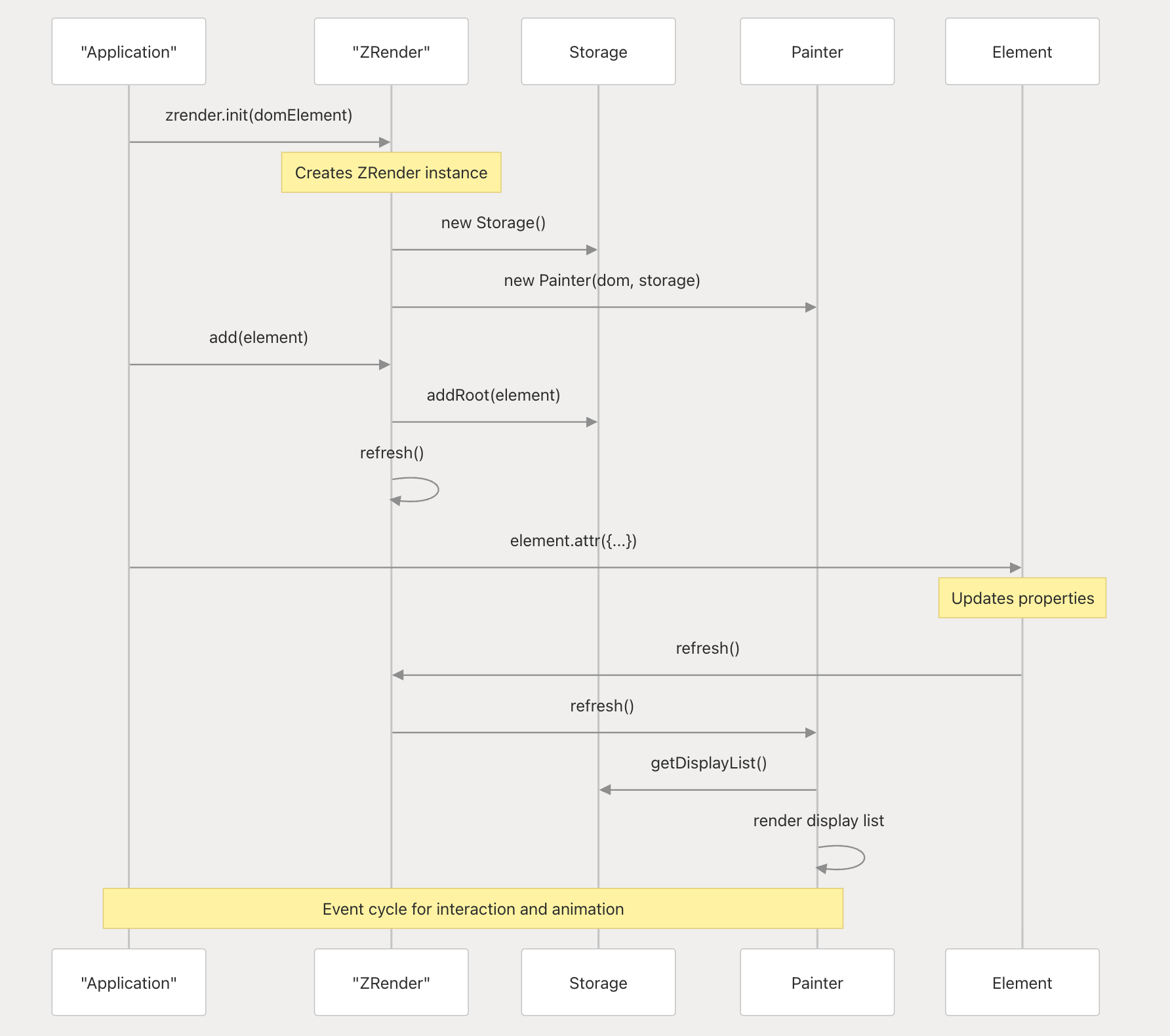
-
Element System:
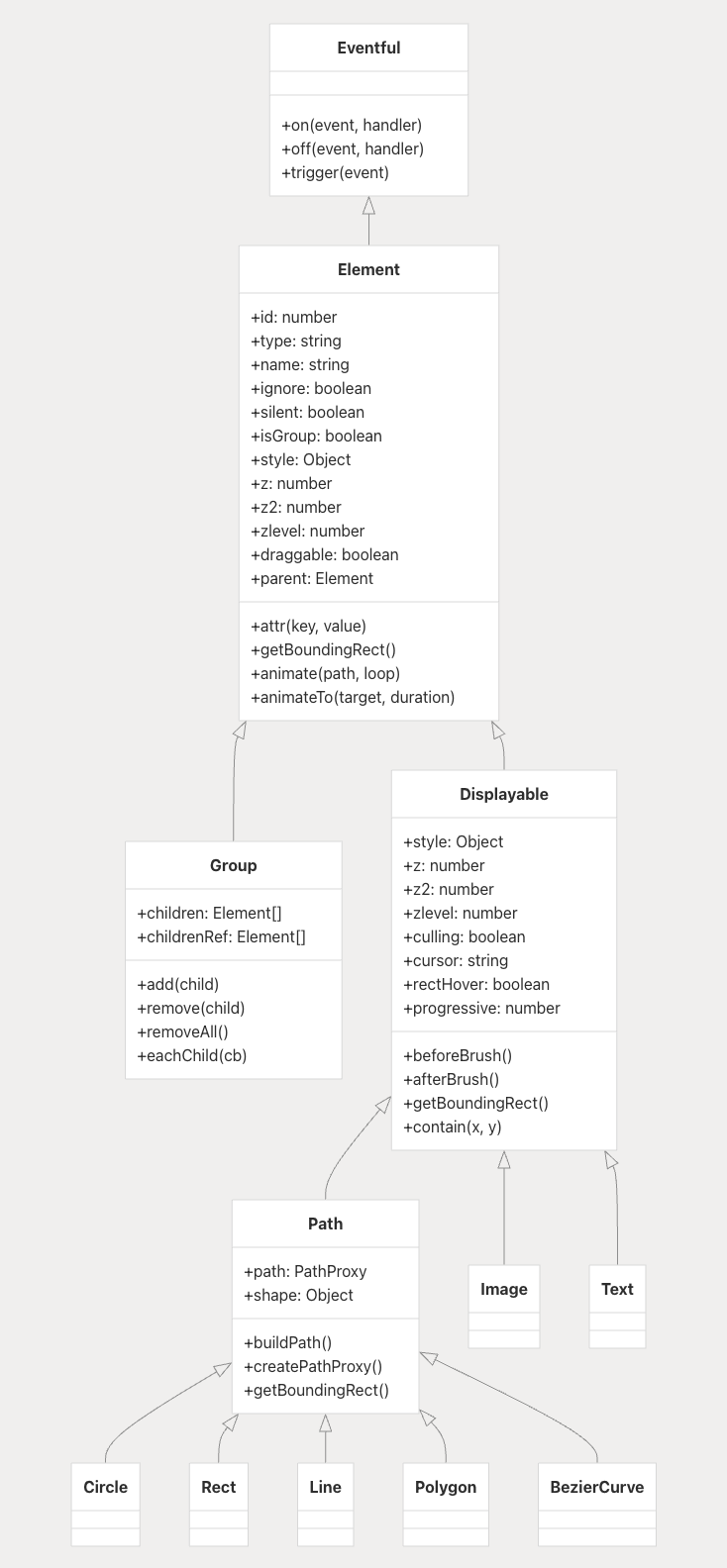
-
Rendering System:
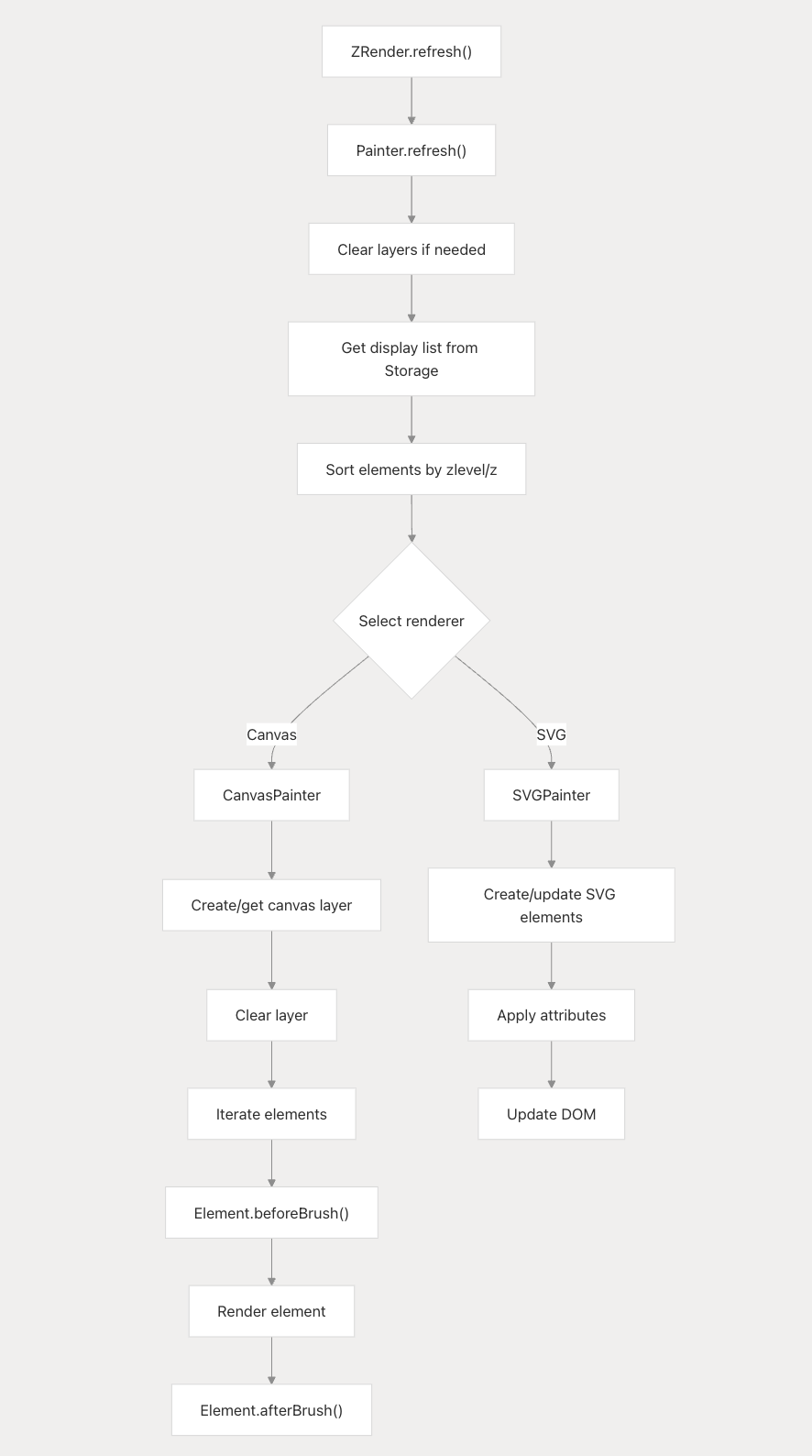
-
Event Handling:
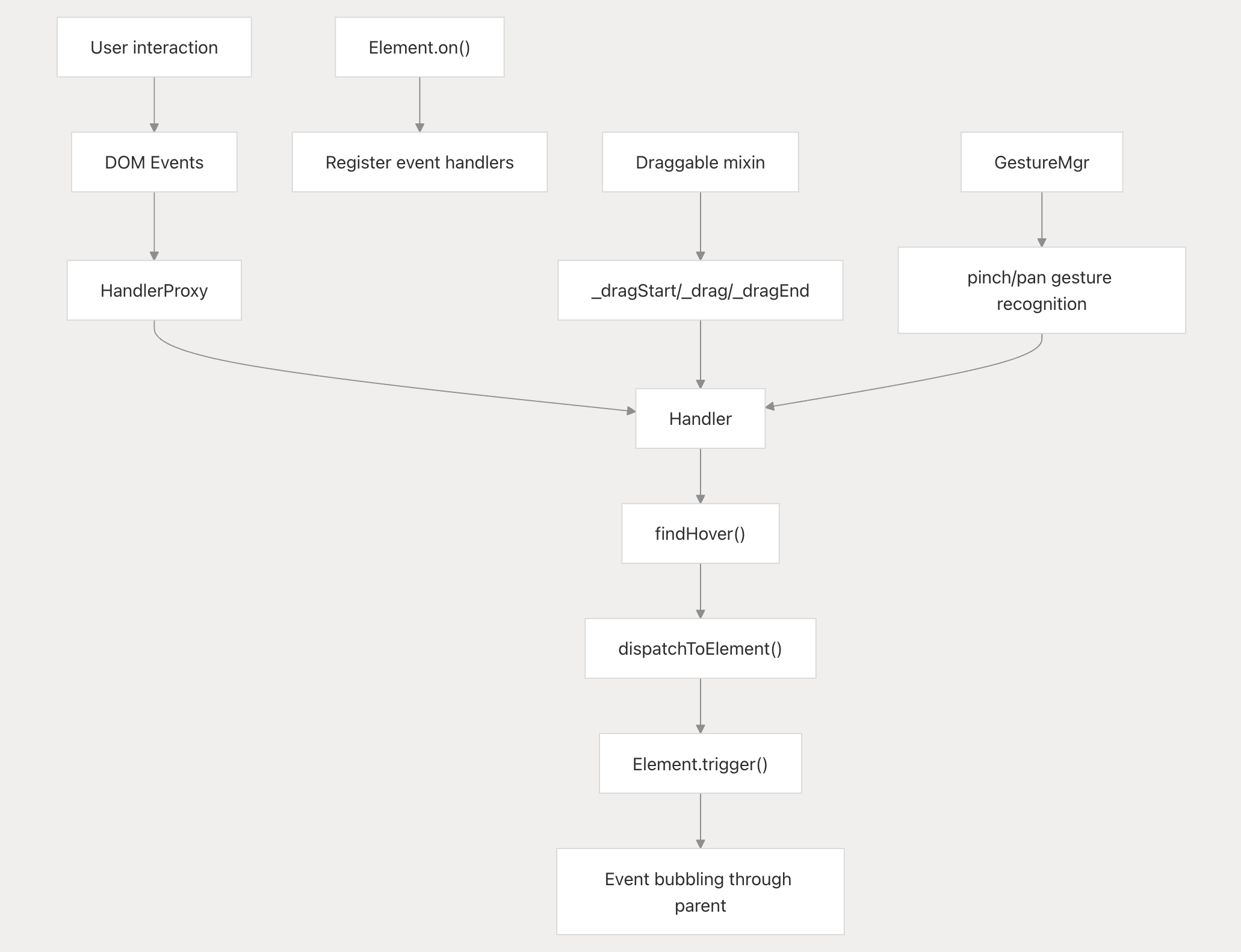
-
Animation System:
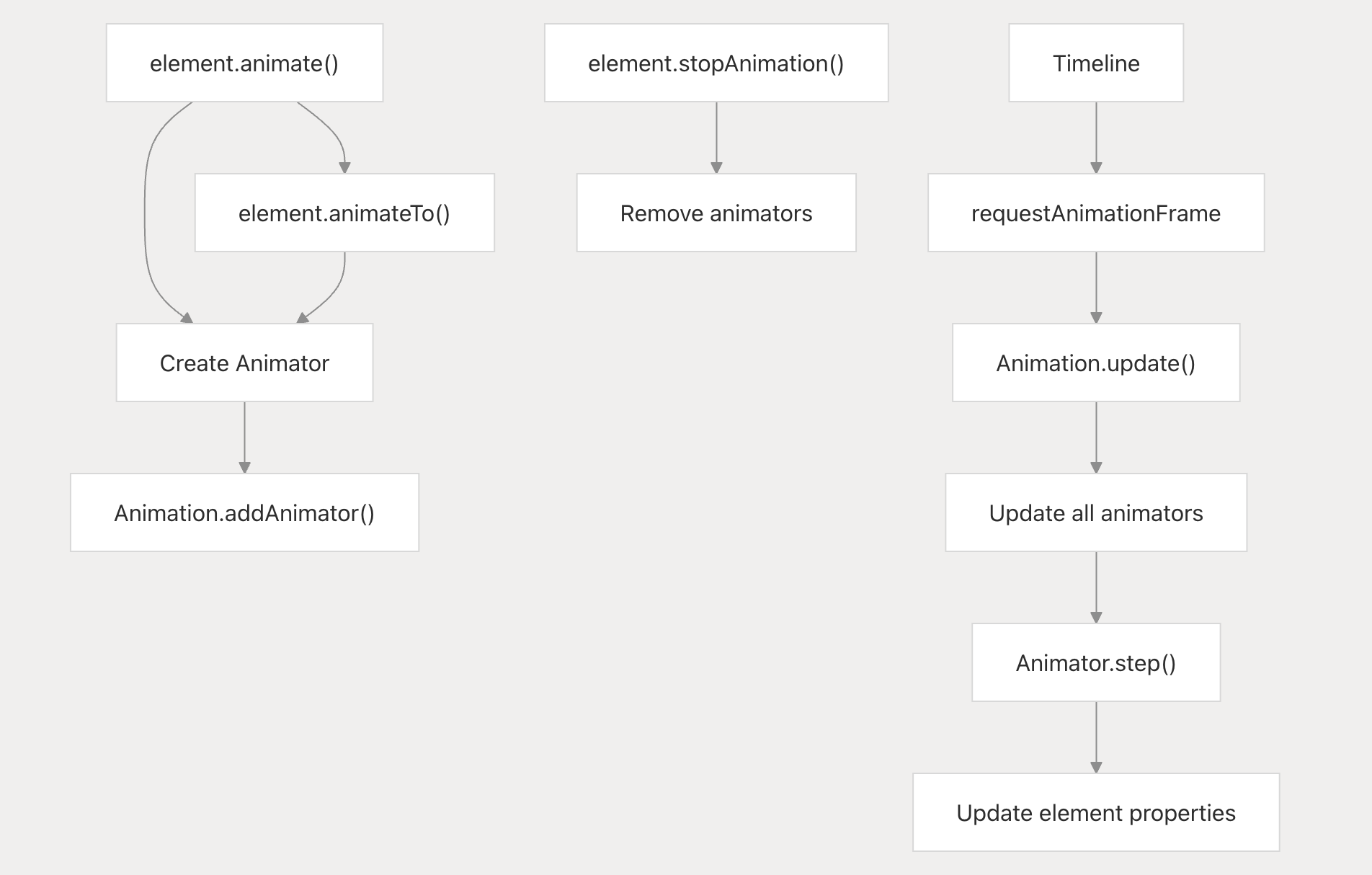
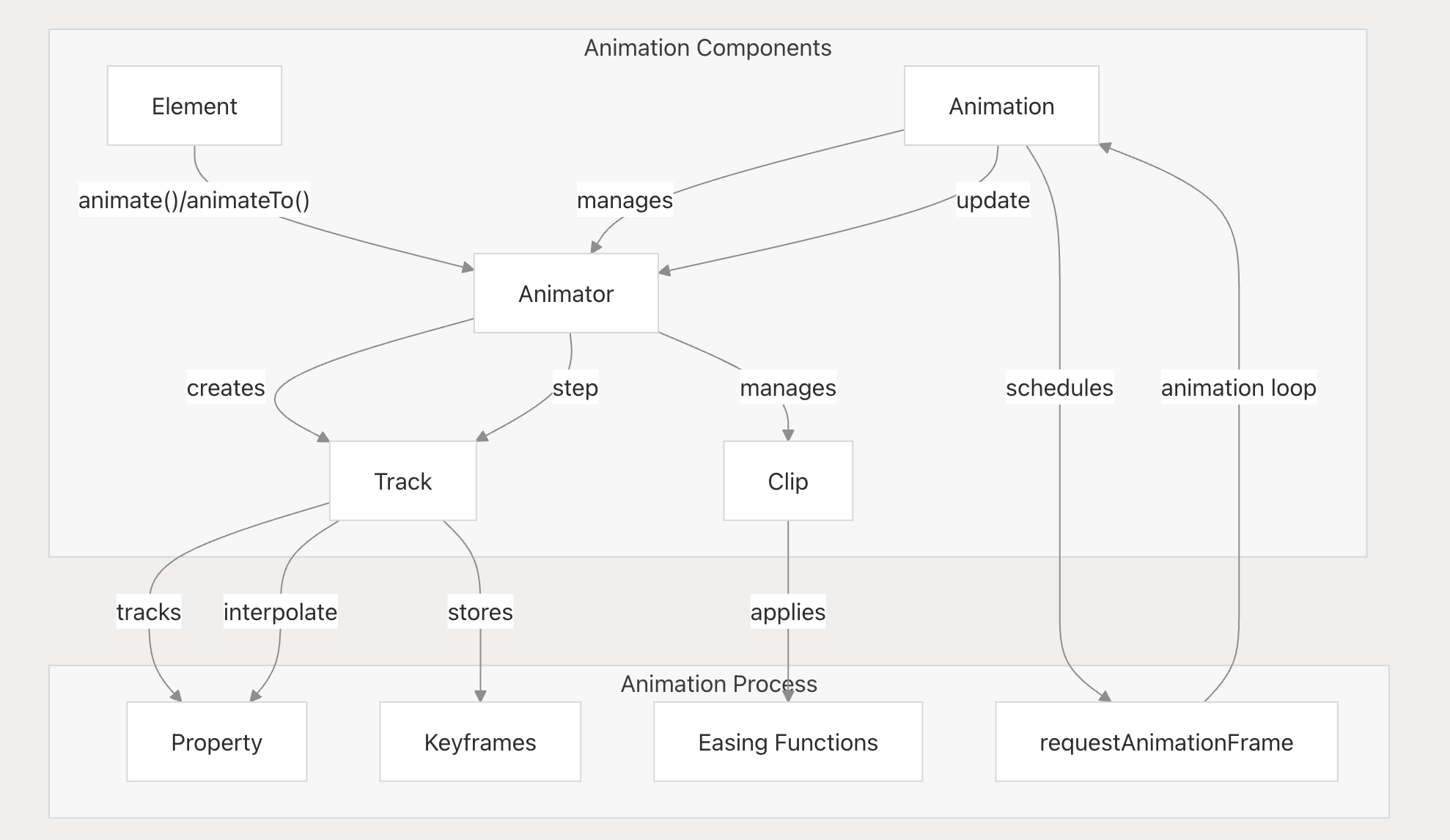 animation render process:
animation render process: